
BMAI
Biomedical Artificial
Intelligence Research Unit

Biomedical Artificial
Intelligence Research Unit
En

Established in June 2021 Read more...

Research Experience:
1993- Hitachi Medical Corporation
1997- Aichi Prefectural University
2001- University of Chicago
2014- Illinois Institute of Technology
2017- Tokyo Institute of Technology
2024- Institute of Science Tokyo
The milestones :
1994 Development and commercialization of early deep learning models Read more...

Server Room
GPU Servers for Research x21
- i9-10980XE 18-Core/3.0GHz; RTX A6000x2; 128GB MEM; SSD 3.8TBx4 HDD 18TBx2
- i9-10940X 14-Core/3.3GHz; RTX 3090×2; 64GB MEM; SSD 960GB
- i9-10940X 14-Core/3.3GHz; RTX A6000; 64GB MEM; SSD 480GB
- EPYC 7502P 32-Core/2.5GHz; RTX A6000x4; 128GB MEM; SSD 1.9TB Read more...

Our paper related to the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), “Explainability of deep learning with modular models” project, had received the most prestigious Magna Cum Laude Award! Read more...

Our paper related to the “Development of knowledge-embedding deep learning and its application to computer-aided diagnostic systems” project by Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), had received the prestigious Cum Laude Award! Read more...

The conventional noise-reduction filters tend to blur the edge information while noise is reduced. To address this issue, we developed a supervised nonlinear filter based on an artificial neural network (ANN), called a “neural filter,” for reduction of noise in images. The neural filter is trained with input images and the corresponding teaching images. To reduce noise in images, we created Read more...
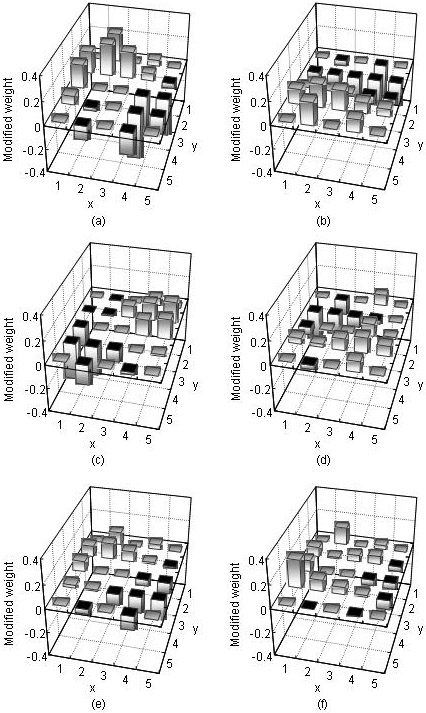
In order to gain insight into the internal presentation of a trained neural edge enhancer, we developed an analysis method for the nonlinear kernel of a trained neural edge enhancer. We trained a neural edge enhancer to enhance edges in noisy images. Our analysis method was applied to the trained neural edge enhancer with a five-by-five-pixel input kernel. Six graphs obtained by the analysis, w Read more...
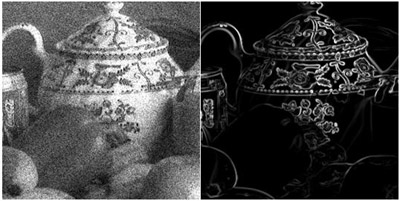
We propose a new edge enhancer based on a modified multilayer neural network, which is called a “neural edge enhancer” (NEE), for enhancing the desired edges clearly from noisy images. The NEE is a supervised edge enhancer: through training with a set of input noisy images and teaching edges, the NEE acquires the function of a desired edge enhancer. The input images are synthesized from noi Read more...
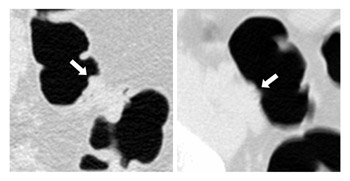
We developed computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) scheme for detection of polyps in CT colonography (CTC) and evaluating our CAD scheme with false-negative polyps in a large multicenter clinical trial in collaboration with Don C. Rockey, M.D., the Southwest Medical Center at the University of Texas. A major challenge in CAD schemes for detection of polyps in CTC is the detection of difficultEpolyps Read more...