Reduction of False Positives in a CAD Scheme for Detection of Lung Nodules on MDCT by Use of 3D Massive-Training Artificial Neural Network
A major challenge in computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) schemes for lung nodule detection in multi-detector-row CT (MDCT) is to reduce false positives (FPs) while maintaining a high sensitivity level. Our purpose in this study was to develop a three-dimensional (3D) massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN) for reduction of FPs. To process quasi-isotropic voxels in the 3D MDCT volume, we developed a 3D MTANN with a 3D input kernel. For distinction between nodules and non-nodules (FPs), the 3D MTANN was trained with input CT volumes and the corresponding teaching volumes that contain a 3D Gaussian distribution for a nodule, and zero for a non-nodule. To remove nine different types of FPs reported by our CAD scheme based on selective enhancement filters with linear discriminant analysis, we developed a multiple 3D MTANN consisting of nine 3D MTANNs. Each 3D MTANN was trained with ten typical nodules and ten non-nodules in each of nine different types of FP sources such as medium-sized vessels, small vessels, vessels with high contrast, and some soft-tissue opacities. Nine MTANNs were combined with the logical AND operation such that nine different types of non-nodules could be eliminated. Our database contained 62 nodules in 32 scans acquired from 32 patients with an MDCT system. The scan consisted of an average of 186 thin-slice CT images (the slice thickness ranged form 1.0 to 2.5 mm). Nodule sizes ranged from 5 to 30 mm. All nodules were confirmed by chest radiologists. With our original CAD scheme, a sensitivity of 96.8% (60/62 nodules) together with an average of 14.9 FPs per case was achieved. The multiple 3D MTANN was applied to further reduction of FPs. The results indicated that 62.2% (296/476) of FPs were removed with a loss of only one true positive. Thus, the FP rate of our original CAD scheme was improved to 5.6 FPs per case at an overall sensitivity of 95.2% (59/62 nodules). By using a multiple 3D MTANN, the specificity of our CAD scheme for lung nodule detection on MDCT can be improved substantially while a high sensitivity is maintained.
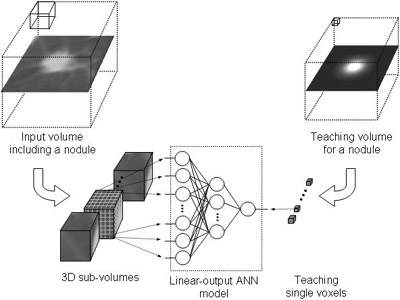
Architecture and training of a three-dimensional massive-training artificial neural network (3D MTANN) for distinction between nodules and non-nodules in MDCT.
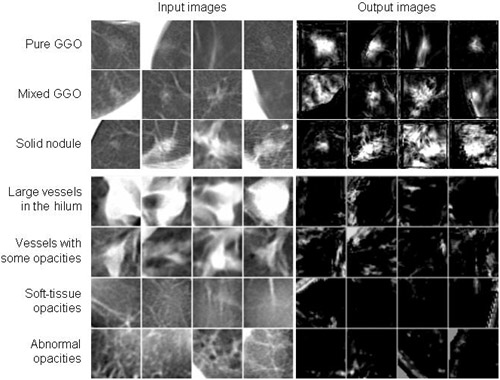
Output images of the trained 3D MTANN for various-sized non-training nodules and vessels in MDCT images.

