
BMAI
バイオメディカルAI研究ユニット

バイオメディカルAI研究ユニット
Ja

バイオメディカルAI研究ユニットは2021年6月に設立されました。 Read more...

研究歴:
1993年- (株) 日立メディコ 技術研究所
1997年- 愛知県立大学 情報科学部
2001年- シカゴ大学 放射線学科/大学院医用物理学研究科/がん研究センター
2014年- イリノイ工科大学 医用画像研究所/電気電子工学研究科
2017年- 東京工業大学 科学技術創成研 Read more...
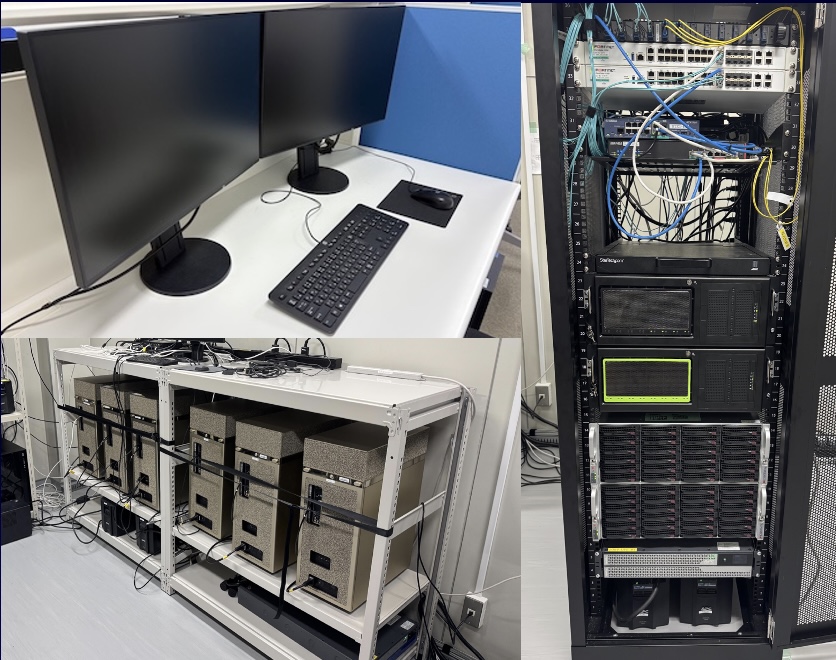

サーバー室
研究用GPUサーバー 21台
- i9-10980XE 18-Core/3.0GHz; RTX A6000x2; 128GB MEM; SSD 3.8TBx4 HDD 18TBx2
- i9-10940X 14-Core/3.3GHz; RTX 3090×2; 64GB MEM; SSD 960GB
- i9-10940X 14-Core/3.3GHz; RTX A6000; 64GB MEM; SSD 480GB
- EPYC 7502P 32-Core/2.5GHz; RTX A6000x Read more...

「JST未来社会事業成果集」が公開されました。 Read more...

新エネルギー・産業技術総合開発機構(NEDO)による人と共に進化する次世代人工知能に関する技術開発事業の「モジュール型モデルによる深層学習のホワイトボックス化」プロジェクトに関連する発表が、RSNA 2024で最高賞の Magna Cum Laude を受賞しました! Read more...

国立研究開発法人科学技術振興機構(JST)未来社会創造事業による「Engineerable AI技術による機械学習応用システムの高信頼化」プロジェクトに関連する発表が、RSNA 2024で最高に次ぐ Cum Laude を受賞しました! Read more...
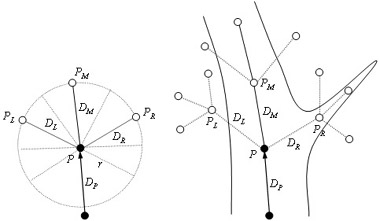
Tracing of vessels is one of the most fundamental techniques in a computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) scheme for vascular systems. A major challenge of methods for tracing vessels is to trace vessels robustly against noise, vessel branching, vessel size changes, and curved vessels, because those factors often lead to errors in tracing. Among them, the robustness against vessel size changes is espec Read more...
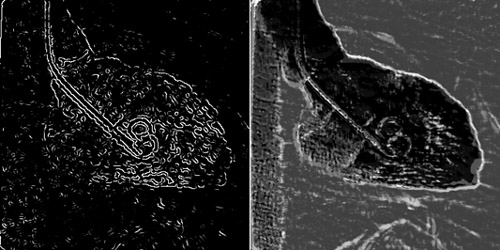
We developed a method for extracting the left ventricular (LV) contours from left ventriculograms by means of a neural edge detector (NED) in order to extract the contours which agree with those traced by a cardiologist. The NED is a supervised edge detector based on a linear-output artificial neural network model, which is trained with a modified back-propagation training algorithm. The NED ca Read more...
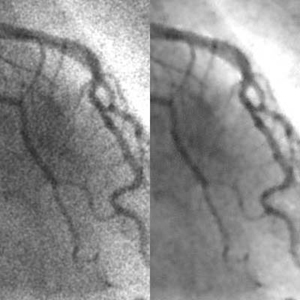
We developed a supervised nonlinear filter based on an artificial neural network (ANN), called a “neural filter,” for reduction of quantum noise in coronary angiograms. The neural filter can be trained with input images and the corresponding teaching images. To learn the relationship between low-dose and high-dose x-ray images, we created simulated low-dose angiograms from actual high-dose Read more...