
BMAI
バイオメディカルAI研究ユニット

バイオメディカルAI研究ユニット
Ja
深層/機械学習

The conventional noise-reduction filters tend to blur the edge information while noise is reduced. To address this issue, we developed a supervised nonlinear filter based on an artificial neural network (ANN), called a “neural filter,” for reduction of noise in images. The neural filter is trained with input images and the corresponding teaching images. To reduce noise in images, we created Read more...
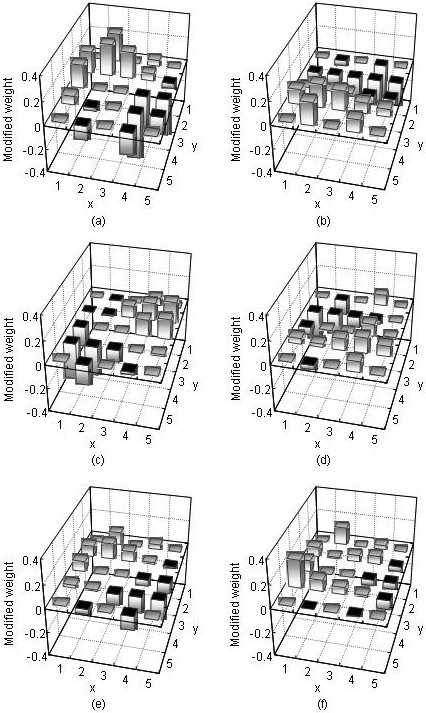
In order to gain insight into the internal presentation of a trained neural edge enhancer, we developed an analysis method for the nonlinear kernel of a trained neural edge enhancer. We trained a neural edge enhancer to enhance edges in noisy images. Our analysis method was applied to the trained neural edge enhancer with a five-by-five-pixel input kernel. Six graphs obtained by the analysis, w Read more...
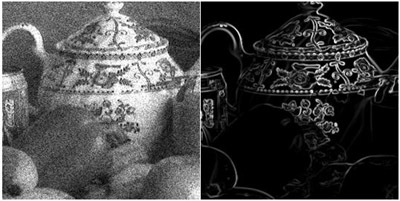
We propose a new edge enhancer based on a modified multilayer neural network, which is called a “neural edge enhancer” (NEE), for enhancing the desired edges clearly from noisy images. The NEE is a supervised edge enhancer: through training with a set of input noisy images and teaching edges, the NEE acquires the function of a desired edge enhancer. The input images are synthesized from noi Read more...
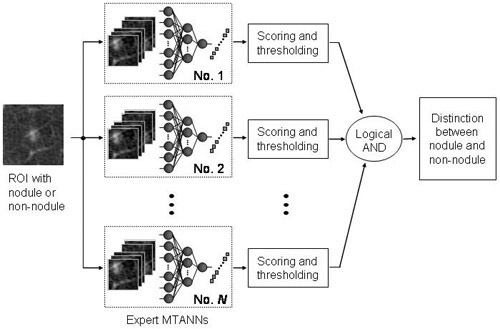
We extended the capability of a single massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN) and developed a multiple MTANN scheme (multi-MTANN) for further removal of false positives (FPs) in computerized detection of lung nodules in low-dose CT. The multi-MTANN consists of several MTANNs arranged in parallel. Each MTANN is trained by use of the same nodules, but with a different type of non-nodu Read more...
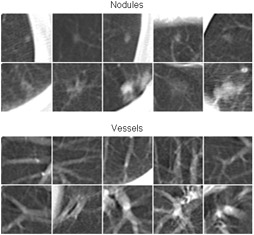
A massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN) is a trainable, highly nonlinear filter consisting of a linear-output multilayer artificial neural network model. For enhancement of nodules and suppression of vessels, we used 10 nodules and 10 non-nodule images as training cases for MTANNs. The MTANN is trained with a large number of input subregions selected from the training cases and the Read more...
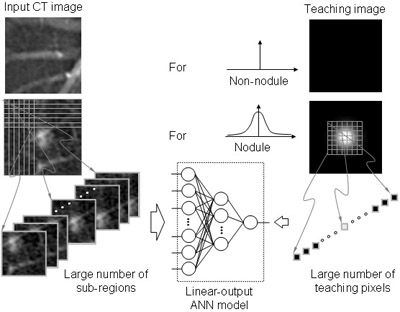
We investigated a novel pattern-recognition technique based on an artificial neural network (ANN), called a massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN), for reduction of false positives (FPs) in computerized detection of lung nodules in low-dose CT. The MTANN consists of a linear-output multilayer ANN model, which is capable of operating on image data directly. The MTANN is trained by us Read more...