
BMAI
Biomedical Artificial
Intelligence Research Unit

Biomedical Artificial
Intelligence Research Unit
En
Biomedical Imaging (BI)
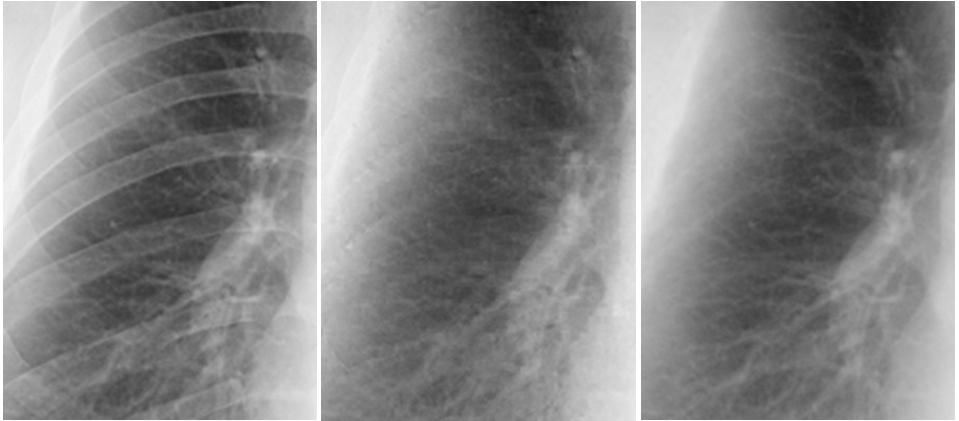
We evaluated our virtual dual-energy radiography technique based on a massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN) in the improvement of the conspicuity of nodules in chest radiographs. To do this, we used a validation test database consisting of 118 chest radiographs with pulmonary nodules and an independent test database consisting of 136 digitized screen-film chest radiographs with 136 Read more...
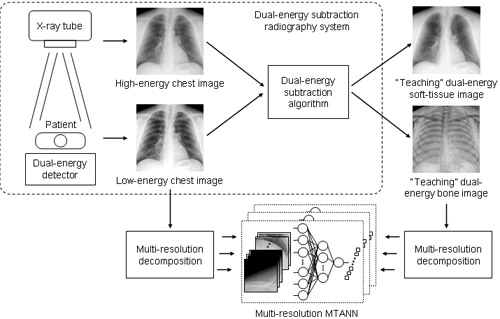
When lung nodules overlap with ribs or clavicles in chest radiographs, it can be difficult for radiologists as well as computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) schemes to detect these nodules. In this study, we developed an image-processing technique for suppressing the contrast of ribs and clavicles in chest radiographs by means of a multi-resolution massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN).< Read more...
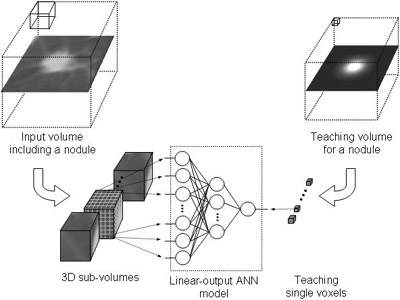
A major challenge in computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) schemes for lung nodule detection in multi-detector-row CT (MDCT) is to reduce false positives (FPs) while maintaining a high sensitivity level. Our purpose in this study was to develop a three-dimensional (3D) massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN) for reduction of FPs. To process quasi-isotropic voxels in the 3D MDCT volume, we Read more...
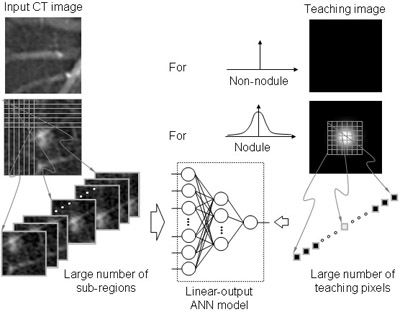
We investigated a novel pattern-recognition technique based on an artificial neural network (ANN), called a massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN), for reduction of false positives (FPs) in computerized detection of lung nodules in low-dose CT. The MTANN consists of a linear-output multilayer ANN model, which is capable of operating on image data directly. The MTANN is trained by us Read more...
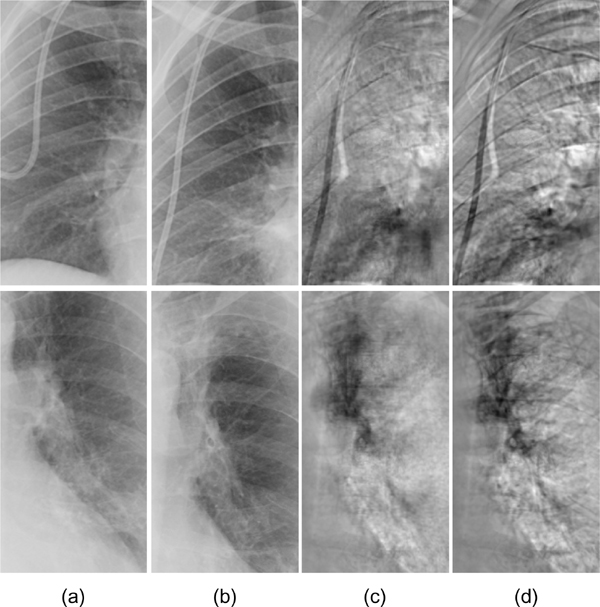
Enhanced Digital Chest Radiography: Temporal Subtraction Combined with Virtual Dual-EnergyETechnology for Improved Conspicuity of Growing Cancers and Other Pathologic Changes
We developed a novel temporal-subtraction (TS) technique combined with virtual dual-energyEtechnology for improved conspicuity of growing cancers and other pathologic changes in digital chest radiography (CXR). Digi Read more...