
BMAI
Biomedical Artificial
Intelligence Research Unit

Biomedical Artificial
Intelligence Research Unit
En
AI-aided Diagnosis

Established in June 2021 Read more...

Research Experience:
1993- Hitachi Medical Corporation
1997- Aichi Prefectural University
2001- University of Chicago
2014- Illinois Institute of Technology
2017- Tokyo Institute of Technology
2024- Institute of Science Tokyo
The milestones :
1994 Development and commercialization of early deep learning models Read more...

Server Room
GPU Servers for Research x21
- i9-10980XE 18-Core/3.0GHz; RTX A6000x2; 128GB MEM; SSD 3.8TBx4 HDD 18TBx2
- i9-10940X 14-Core/3.3GHz; RTX 3090×2; 64GB MEM; SSD 960GB
- i9-10940X 14-Core/3.3GHz; RTX A6000; 64GB MEM; SSD 480GB
- EPYC 7502P 32-Core/2.5GHz; RTX A6000x4; 128GB MEM; SSD 1.9TB Read more...
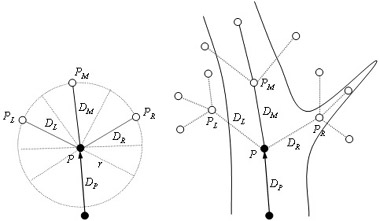
Tracing of vessels is one of the most fundamental techniques in a computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) scheme for vascular systems. A major challenge of methods for tracing vessels is to trace vessels robustly against noise, vessel branching, vessel size changes, and curved vessels, because those factors often lead to errors in tracing. Among them, the robustness against vessel size changes is espec Read more...
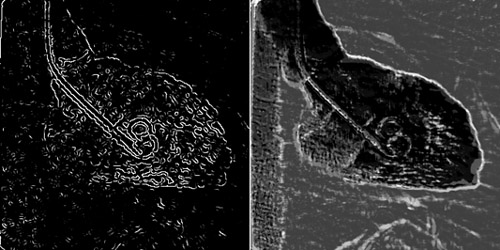
We developed a method for extracting the left ventricular (LV) contours from left ventriculograms by means of a neural edge detector (NED) in order to extract the contours which agree with those traced by a cardiologist. The NED is a supervised edge detector based on a linear-output artificial neural network model, which is trained with a modified back-propagation training algorithm. The NED ca Read more...
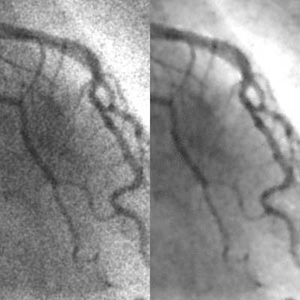
We developed a supervised nonlinear filter based on an artificial neural network (ANN), called a “neural filter,” for reduction of quantum noise in coronary angiograms. The neural filter can be trained with input images and the corresponding teaching images. To learn the relationship between low-dose and high-dose x-ray images, we created simulated low-dose angiograms from actual high-dose Read more...
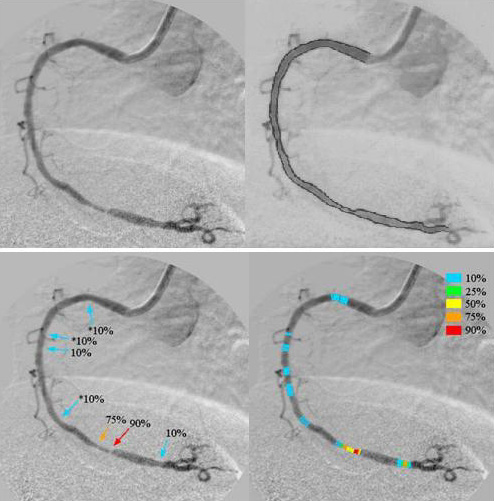
We developed a new computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) system for coronary artery stenosis, which can learn physicians’ diagnosis. To realize such a system, we developed a linear-output artificial neural network (LOANN) which is capable of learning of experts’ judgment. Our CAD system consisted of (a) an automated method for tracing vessels, (b) a robust method for determining the edges of the Read more...
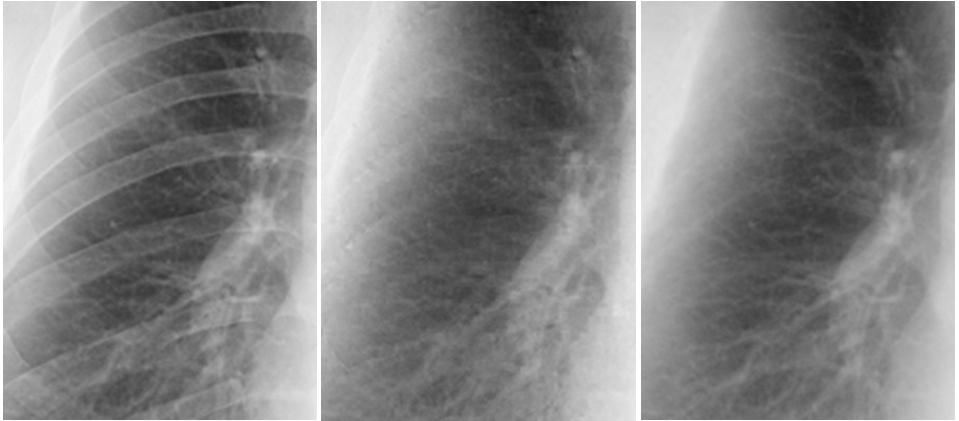
We evaluated our virtual dual-energy radiography technique based on a massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN) in the improvement of the conspicuity of nodules in chest radiographs. To do this, we used a validation test database consisting of 118 chest radiographs with pulmonary nodules and an independent test database consisting of 136 digitized screen-film chest radiographs with 136 Read more...
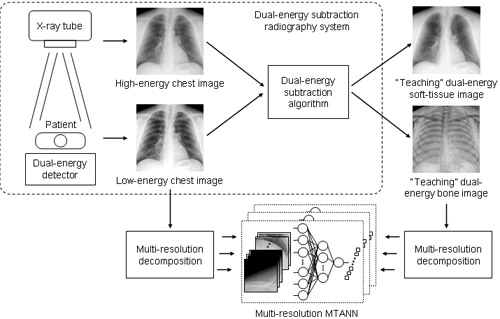
When lung nodules overlap with ribs or clavicles in chest radiographs, it can be difficult for radiologists as well as computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) schemes to detect these nodules. In this study, we developed an image-processing technique for suppressing the contrast of ribs and clavicles in chest radiographs by means of a multi-resolution massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN).< Read more...