
BMAI
Biomedical Artificial
Intelligence Research Unit

Biomedical Artificial
Intelligence Research Unit
En
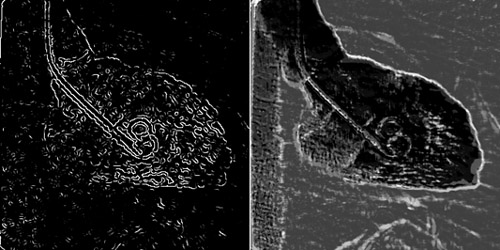
We developed a method for extracting the left ventricular (LV) contours from left ventriculograms by means of a neural edge detector (NED) in order to extract the contours which agree with those traced by a cardiologist. The NED is a supervised edge detector based on a linear-output artificial neural network model, which is trained with a modified back-propagation training algorithm. The NED ca Read more...
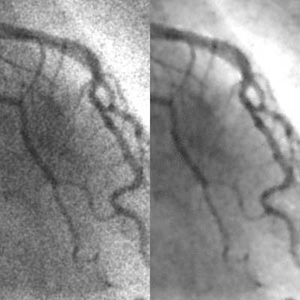
We developed a supervised nonlinear filter based on an artificial neural network (ANN), called a “neural filter,” for reduction of quantum noise in coronary angiograms. The neural filter can be trained with input images and the corresponding teaching images. To learn the relationship between low-dose and high-dose x-ray images, we created simulated low-dose angiograms from actual high-dose Read more...
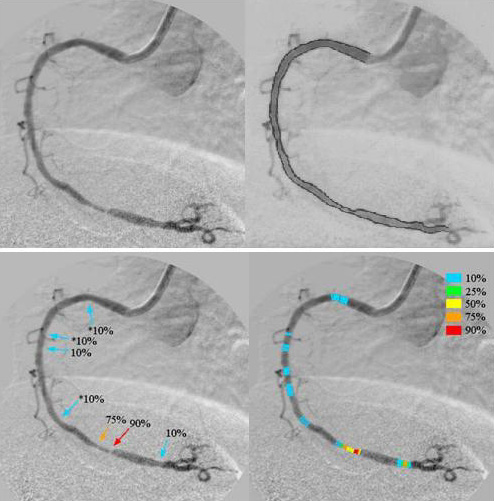
We developed a new computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) system for coronary artery stenosis, which can learn physicians’ diagnosis. To realize such a system, we developed a linear-output artificial neural network (LOANN) which is capable of learning of experts’ judgment. Our CAD system consisted of (a) an automated method for tracing vessels, (b) a robust method for determining the edges of the Read more...
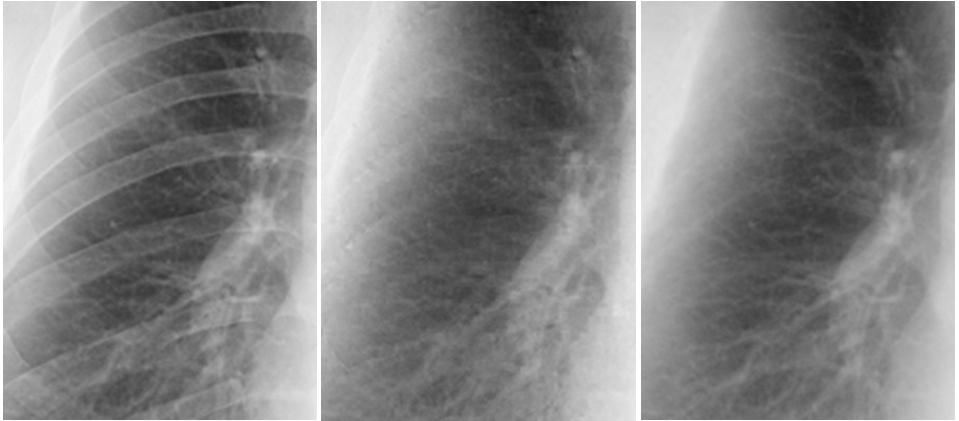
We evaluated our virtual dual-energy radiography technique based on a massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN) in the improvement of the conspicuity of nodules in chest radiographs. To do this, we used a validation test database consisting of 118 chest radiographs with pulmonary nodules and an independent test database consisting of 136 digitized screen-film chest radiographs with 136 Read more...
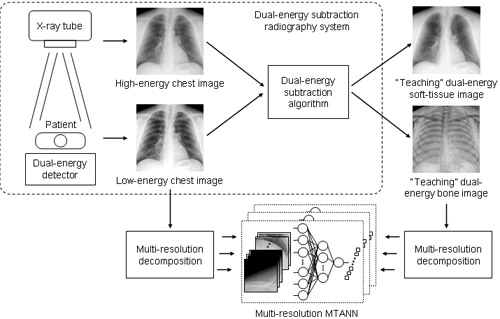
When lung nodules overlap with ribs or clavicles in chest radiographs, it can be difficult for radiologists as well as computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) schemes to detect these nodules. In this study, we developed an image-processing technique for suppressing the contrast of ribs and clavicles in chest radiographs by means of a multi-resolution massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN).< Read more...
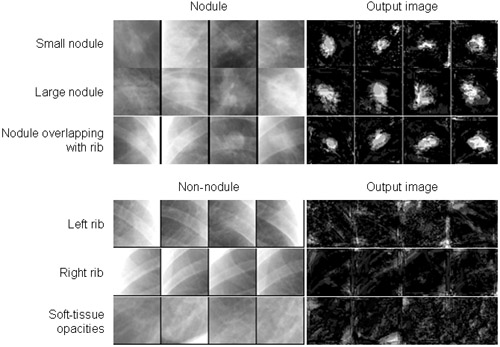
We developed a technique that uses a multiple massive-training artificial neural network scheme (multi-MTANN) to reduce false positives (FPs) in a computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) scheme for nodule detection on chest radiographs. Our database consisted of 91 solitary pulmonary nodules including 64 malignant nodules and 27 benign nodules in 91 chest radiographs. With our CAD scheme based on a dif Read more...
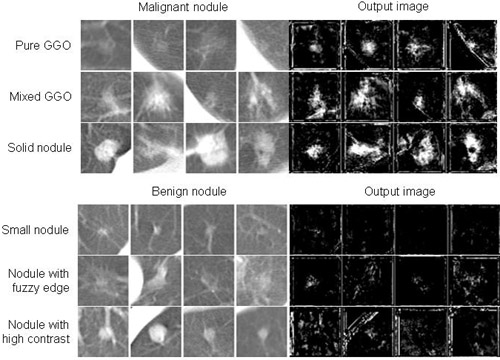
Low-dose helical CT (LDCT) is being applied as a modality for lung cancer screening. It may be difficult, however, for radiologists to distinguish malignant from benign nodules in LDCT. Our purpose in this study was to develop a computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) scheme for distinction between benign and malignant nodules in LDCT by use of a massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN). The Read more...
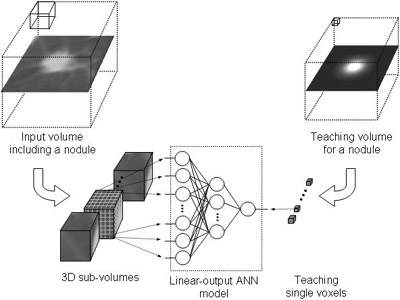
A major challenge in computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) schemes for lung nodule detection in multi-detector-row CT (MDCT) is to reduce false positives (FPs) while maintaining a high sensitivity level. Our purpose in this study was to develop a three-dimensional (3D) massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN) for reduction of FPs. To process quasi-isotropic voxels in the 3D MDCT volume, we Read more...
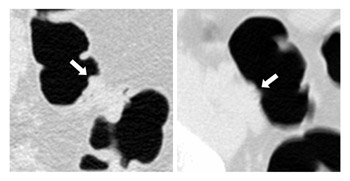
We developed computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) scheme for detection of polyps in CT colonography (CTC) and evaluating our CAD scheme with false-negative polyps in a large multicenter clinical trial in collaboration with Don C. Rockey, M.D., the Southwest Medical Center at the University of Texas. A major challenge in CAD schemes for detection of polyps in CTC is the detection of difficultEpolyps Read more...